Mobile App Sensor Documentation
...
(English Version)
Version: | 12.1.0 |
|---|---|
Date: | 20122015-0809-1625 |
Author: | Frank KammannKantar Media Audiences (DE) |
eMail: |
Content
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Method
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Information for Developers
All spring sensors capture the events in the moment in which they arise. This concept is also implemented in the libraries for the apps, that means that all actions are sent immediately.
In case of any questions concerning this, please contact our support team under support@spring.de.under KA_DE_support@kantarmedia.com
Integration of Libraries
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Release of the Application
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Features on Platforms
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Description of the Mobile App Library Interface
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Properties of the Libraries
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Predefined Variables
Out of the application, an HTTP request has to be sent to the measuring system.
Variable | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
ac | No | The action that has been executed. |
The variable: Action (ac)
By using this variable, the measuring system can be informed, which actions have been executed in the application.
Currently, the following actions are understood:
Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| The application has been started. |
| The application was brought to the foreground or has received the focus. |
| The application was brought into the background or does no longer have the focus. |
| The application has been stopped. |
Implementation of an app page request via the action variable (ac)
By using the variable ac, the execution of a content page within an application can be measured also.
...
- a-z
- A-Z
- 0-9
- Comma “,”
- Point “.”
- Dash “-” and Underscore “_”
| Info |
|---|
Slash "/" is used as separator for hierarchy levels |
...
- sport_football
- mainpage
- 200_543
...
Information (optional)
The user can be informed at some point that the application monitors the user actions and transmits them to a measuring system. Furthermore, the user must be informed that he has the possibility to switch of the tracking in the application and can contradict this way. (see: CIM - Mobile App Sensor Documentation Version 1.1.0 (English Version))For Opt-Out)
For this purpose, you can include data privacy information in your language into an appropriate place of your app implementation:
...
Mobile App Sensor Measurement: |On/Off|
Opt-Out
The application developer can give users the ability to stop the further tracking of the user actions. For this purpose the library offers the following methods:
...
A persistent saving of the opt-out decision in the library is not provided and needs to be implemented by the app developer.
Mobile Support
Should you encounter any issues or problems during the implementation, please send an email to our support team under support@spring.de KA_DE_support@kantarmedia.com with the following information:
- Name
- Description of the problem
- Possibly error messages with error codes
- Platform (version), application name (version)
Supported Platforms
Implementation iOS
...
The following example shows the basic installation for the iOS platform. When generating the class SpringMobile a site identifier (<site>) has to be indicated, which is shipped together with this documentation and the libraries.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
At the application start the Spring object has to be instanced one-time and to be used for the whole life cycle of the application |
...
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/* * Importing SpringMobile */ #import "Spring.h" /* * Providing entity */ Spring *spring; /* * Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and * application name */ spring = [[Spring alloc] initWithSiteAndApplication:@"<site>" application:@"myApplication1"]; /* * Sending the start of the application to the measurement system */ NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:APP_STARTED,VAR_ACTION,nil]; [spring commit:dict]; ... // OR /* * Sending the action spring.BACKGROUND */ NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:APP_BACKGROUND,VAR_ACTION,nil]; [spring commit:dict]; |
...
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/* * Importing SpringMobile */ #import "Spring.h" /* * Providing entity */ Spring *spring; /* * Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and application name */ spring = [[Spring alloc] initWithSiteAndApplication:@"<site>" application:@"myApplication1"]; /* * Sending AC to the measurement system */ NSMutableDictionary *dict = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:@"Mainpage",@"ac",nil]; [spring commit:dict]; ... |
Timeout
...
With this value, a timeout (in seconds = default: 30 seconds)) for each HTTP request can be configured within the library.
...
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
spring = [[Spring alloc] initWithSiteAndApplication:@"app" application:@"Test App"]; spring.timeout = 30.0; // in seconds |
Debug
If this value is set on YES, the library provides debug outputs over the class NSLog.
...
| No Format |
|---|
2011-11-25 13:42:52.878 TestApp3[73923:ff07] spring (1.0.3.1)> http://test.2cnt.net/j0=,,,;+,app=Test%20App+did=7ca359bc4c3c6a19;;;?lt=gvf6lykt 2011-11-25 13:42:52.927 TestApp3[73923:ff07] spring (1.0.3.1)> http status code: 200 - no error 2011-11-25 13:42:56.521 TestApp3[73923:1020b] spring (1.0.3.1)> http://test.2cnt.net/j0=,,,;+,app=Test%20App+did=7ca359bc4c3c6a19+ac=spring.BACKGROUND;;;?lt=gvf6m1e1 2011-11-25 13:42:56.559 TestApp3[73923:1020b] spring (1.0.3.1)> http status code: 200 - no error 2011-11-25 13:42:59.388 TestApp3[73923:10013] spring (1.0.3.1)> http://test.2cnt.net/j0=,,,;+,app=Test%20App+did=7ca359bc4c3c6a19+ac=spring.FOREGROUND;;;?lt=gvf6m3lo 2011-11-25 13:42:59.427 TestApp3[73923:10013] spring (1.0.3.1)> http status code: 200 - no error 2011-11-25 13:43:04.554 TestApp3[73923:11f0b] spring (1.0.3.1)> http://test.2cnt.net/j0=,,,;+,app=Test%20App+did=7ca359bc4c3c6a19+ac=spring.BACKGROUND;;;?lt=gvf6m7l5 |
...
Implementation
...
The following example shows the basic installation for the Android platform. When generating the class SpringMobile a site identifier (<site>) has to be indicated, which is shipped together with this documentation and the libraries.
Example:
...
| language | java |
|---|
...
of the URL Scheme in iOS
Generally for spring measuring purpose, only some modifications need to be applied in your App, if a Panel App is used in your market.
(This blog may assist your implementation):
Register the URL Scheme accordingly.
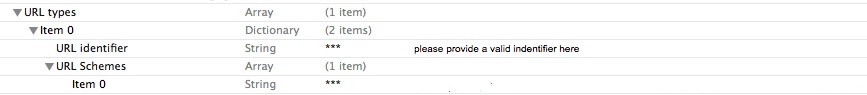
In order to register your URL Scheme into your iOS App, you need to edit the Info.plist file under the "Supporting Files" in your project folder, two ways:
you can edit it in any editor, if you do so, please insert the following code:
Code Block <key>CFBundleURLTypes</key> <array> <dict> <key>CFBundleURLName</key> <string>***</string> //please change *** to your URL name, not so important <key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key> <array> <string>***</string> //very important, please replace </array> </dict> </array>Or you can edit this in xcode, add an item into
Info.plist, named "URL types", expand "Item 0" under "URL types", and add two items: "URL identifier", "URL Schemes".For "URL identifier", assign your identifier, and for "URL Schemes", add a new item within it named "Item0", REGISTER A UNIQUE URL SCHEME FOR YOUR APP, VERY IMPORTANT!
It should be like the following:
How to use the different Files in the Library Package
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| spring-appsensor-device.a | This is the version that has been compiled with ARM support and which is intended for execution on iOS devices |
| spring-appsensor-simulator.a | This is the version that has been compiled with x86 support and which is intended for execution on iOS simulator |
| spring-appsensor-fat.a | This is a combined version of the two libraries above, which can be executed on both, iOS devices and iOS simulator because it contains code for ARM and x86 execution. This file is called "fat" as it is roughly double the size (because it combines both versions). |
| Note |
|---|
If size does not matter for the app, the "fat" version is the carefree option to be used for execution on simulator and real devices. |
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Implementation Android
The following example shows the basic installation for the Android platform. When generating the class SpringMobile a site identifier (<site>) has to be indicated, which is shipped together with this documentation and the libraries.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/**
* Importing SpringMobile
*/
import de.spring.mobile.SpringMobile;
/**
* Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and
* application name
*/
SpringMobile spring = new SpringMobile("<site>", "Application Name", getApplicationContext());
/**
* Sending the start of the application to the measurement system
*/
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_STARTED);
spring.commit(map);
/*
* Sending the action spring.BACKGROUND
*/
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUND);
spring.commit(map);
|
Managing Lifecycle Events in Android Apps
A helper class for the Activities can be used instead of SpringMobile.
Link: http://developer.android.com/reference/android/app/Activity.html
| Code Block |
|---|
Example Activity: import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; public class TestActivity extends Activity { private SpringMobileHelper springHelper; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); springHelper = SpringMobileHelper.getInstance(getApplicationContext()); } @Override protected void onStart() { super.onStart(); springHelper.start(); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); springHelper.resume(); } @Override protected void onPause() { super.onPause(); springHelper.pause(); } @Override protected void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); springHelper.destroy(); } } Helper Class: import java.lang.Thread.State; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import android.content.Context; import de.spring.mobile.SpringMobile; /** This class will help to manage more than one Activity. The Class holds the SpringMobile object and managed the events to it. */ public class SpringMobileHelper { private static SpringMobileHelper singelton = null; private SpringMobile spring = null; private boolean isStarted = false; private int foregroundCounter = 0; private final Thread sendBackground = new Thread() { @Override public void run() { super.run(); while(true) { synchronized(sendBackground) { try { wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { continue; } try { sleep(1000); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUND); spring.commit(map); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} } } } }; {sendBackground.start();} private SpringMobileHelper() { } /** * @param the context @return SpringMobileHelper */ public static SpringMobileHelper getInstance(Context context) Unknown macro: { if(singelton == null) { singelton = new SpringMobileHelper(); singelton.spring = new SpringMobile("app", "MoreActivities", context); } return singelton; } /** call by start of activity */ public void start() Unknown macro: { if(!isStarted) { isStarted = true; Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); spring.commit(map); } } /** call by resume of activity */ public void resume() Unknown macro: { foregroundCounter++; if(sendBackground != null && sendBackground.getState() != State.WAITING) { sendBackground.interrupt(); } else { Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_FOREGROUND); spring.commit(map); } } /** * call by pause of activity */ public void pause() { foregroundCounter--; if(sendBackground != null && sendBackground.getState() != State.WAITING) { sendBackground.interrupt(); } } synchronized(sendBackground) { sendBackground.notify(); } } /** call by destroy of activity */ public void destroy() { if(foregroundCounter == 0) { try { sendBackground.join(1000); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map map.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUNDCLOSED); spring.commit(map); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} } } } |
Example: Implementation of an app page request via the action variable (ac)
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/**
* Example AC
*/
import de.spring.mobile.SpringMobile;
/**
* Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and application name
*/
SpringMobile spring = new SpringMobile("<site>", "Application Name", getApplicationContext());
/**
* Sending AC to the measurement system
*/
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("ac", "Mainpage");
spring.commit(map);
|
...
Android Permissions
The following settings need to be conducted in the file AndroidManifest.xml AndroidManifest.xml:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE"> </uses-permission> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"> </uses-permission> </uses-permission> <meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> |
| Info |
|---|
The setting of the permission through the user is not mandatory, but highly recommended. If the permission If the permission is not set, only the Android ID is used. The last one item above is for the registration of google-play-services, which is precondition for retrieving Google Advertising ID. Two aspects are crucial: There is a bug in the Android version 2.2, which only occurs in connection with certain providers, where for all affected devices the same Android ID will be delivered. For the study, this would mean that the user identification would become much more difficult. |
Timeout
With this value, a timeout (in seconds) for each HTTP request can be configured within the library.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
SpringMobile spring = new ("app","TestApp",getApplicationContext());
spring.setTimeout(30); // in seconds
|
Advise for Implementation when using Android 3.0 and higher Versions
| Note |
|---|
Note: |
...
|
...
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
class CommitTask extends AsyncTask<Map<String,Object>, Void, Void> {
protected Void doInBackground(Map<String,Object>... params) {
if(params.length != 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("one parameter expected");
spring.commit(params[0]);
return null;
}
} |
...
not allowed from the main thread anymore. Thus, the Spring.commit () method is achieved in a background thread. For this reason, please keep the initialization and usage of Spring lib in your main UI thread, Spring lib will not block your GUI display. Otherwise background thread conflicts might pop up. |
ProGuard
Therefore it is necessary to add the following lines into the ProGuard configuration file:
-keep class de.spring.** { *; }
-keep class de.spring.** { *; }
-keep class org.apache.** { *; }
If you want to suppress the warnings regarding library-program-class-dependencies , please add to the configuration file
-dontwarn android.webkit.WebView
-dontwarn android.webkit.WebViewClient
Implementation Blackberry
The following example shows the basic installation for the Blackberry platform. When generating the class SpringMobile a site identifier (<site>) has to be indicated, which is shipped together with this documentation and the libraries.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/**
* Importing SpringMobile
*/
import de.spring.mobile.SpringMobile;
/**
* Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and
* application name
*/
SpringMobile spring = new SpringMobile("<site>", "myApplication1");
/**
* Sending the start of the application to the measurement system
*/
Hashtable target = new Hashtable();
target.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_STARTED);
try {
// ...
spring.commit(target);
} catch (ParamNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* Sending the action spring.BACKGROUND
*/
Hashtable target = new Hashtable();
target.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUND);
try {
spring.commit(target);
} catch (ParamNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
 |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/**
* Alternative method
* Sending the action spring.BACKGROUND with own
* connection parameters
*/
Hashtable target = new Hashtable();
target.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUND);
Hashtable bbprops = new Hashtable();
bbprops.put("deviceside", "true");
try {
spring.commit(bbprops,target);
} catch (ParamNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
Example: Implementation of an app page request via the action variable (ac)
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/**
* example AC
*/
Hashtable target = new Hashtable();
target.put("ac", "Mainpage");
try {
// ...
spring.commit(target);
} catch (ParamNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
| Info |
|---|
Although the library provides the possiblity of using connection parameters, it is highly recommended to use "spring.commit(Hashtable target)". While using connection parameters that are not supported a respective exception is thrown. |
Implementation Windows Phone
The following example shows the basic installation for the Windows Phone 7 platform. When generating the class SpringMobile a site identifier (<site>) has to be indicated, which is shipped together with this documentation and the libraries.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/*
* Importing SpringMobile
*/
using spring_mobile_wp7;
/*
* Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and
* application name
*/
SpringMobile spring = new SpringMobile("<site>", "myApplication1");
/*
* Sending the start of the application to the measurement system
*/
Dictionary<String, String> target = new Dictionary<string, string>();
target.Add(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_STARTED);
spring.commit(target);
...
/*
* Sending the action spring.BACKGROUND
*/
Dictionary<String, String> target = new Dictionary<string, string>();
target.Add(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUND);
spring.commit(target);
|
Example: Implementation of an app page request via the action variable (ac)
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/*
* Example AC
*/
using spring_mobile_wp7;
/*
* Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and application name
*/
SpringMobile spring = new SpringMobile("<site>", "myApplication1");
/*
* Sending AC to the measurement system
*/
Dictionary<String, String> target = new Dictionary<string, string>();
target.Add("ac", "Mainpage");
spring.commit(target);
...
/*
|
| Info | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
For the measurement we need the device ID. Please set the right for reading the device ID into a config file (WMAppManifest.xml).
|
Implementation Titanium (not supported at the moment)
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|