...
you can edit it in any editor, if you do so, please insert the following code:
Code Block <key>CFBundleURLTypes</key> <array> <dict> <key>CFBundleURLName</key> <string>***</string> //please change *** to your URL name, not so important <key>CFBundleURLSchemes</key> <array> <string>***</string> //very important, please replace </array> </dict> </array>
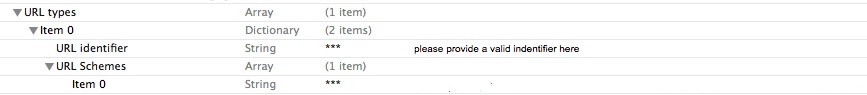
Or you can edit this in xcode, add an item into
Info.plist, named "URL types", expand "Item 0" under "URL types", and add two items: "URL identifier", "URL Schemes".For "URL identifier", assign your identifier, and for "URL Schemes", add a new item within it named "Item0", REGISTER A UNIQUE URL SCHEME FOR YOUR APP, VERY IMPORTANT!
It should be like the following:
Implementation Android
The following example shows the basic installation for the Android platform. When generating the class SpringMobile a site identifier (<site>) has to be indicated, which is shipped together with this documentation and the libraries.
Example
...
| language | java |
|---|
...
How to use the different Files in the Library Package
| File | Description |
|---|---|
| spring-appsensor-device.a | This is the version that has been compiled with ARM support and which is intended for execution on iOS devices |
| spring-appsensor-simulator.a | This is the version that has been compiled with x86 support and which is intended for execution on iOS simulator |
| spring-appsensor-fat.a | This is a combined version of the two libraries above, which can be executed on both, iOS devices and iOS simulator because it contains code for ARM and x86 execution. This file is called "fat" as it is roughly double the size (because it combines both versions). |
| Note |
|---|
If size does not matter for the app, the "fat" version is the carefree option to be used for execution on simulator and real devices. |
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Implementation Android
The following example shows the basic installation for the Android platform. When generating the class SpringMobile a site identifier (<site>) has to be indicated, which is shipped together with this documentation and the libraries.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/**
* Importing SpringMobile
*/
import de.spring.mobile.SpringMobile;
/**
* Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and
* application name
*/
SpringMobile spring = new SpringMobile("<site>", "Application Name", getApplicationContext());
/**
* Sending the start of the application to the measurement system
*/
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_STARTED);
spring.commit(map);
/*
* Sending the action spring.BACKGROUND
*/
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUND);
spring.commit(map);
|
...
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE">
</uses-permission>
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET">
</uses-permission>
<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> |
| Info |
|---|
The setting of the permission through the user is not mandatory, but highly recommended. If the permission If the permission is not set, only the Android ID is used. The last one item above is for the registration of google-play-services, which is precondition for retrieving Google Advertising ID. Two aspects are crucial: There is a bug in the Android version 2.2, which only occurs in connection with certain providers, where for all affected devices the same Android ID will be delivered. For the study, this would mean that the user identification would become much more difficult. |
Timeout
With this value, a timeout (in seconds) for each HTTP request can be configured within the library.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
SpringMobile spring = new ("app","TestApp",getApplicationContext());
spring.setTimeout(30); // in seconds
|
Advise for Implementation when using Android 3.0 and higher Versions
| Note |
|---|
Note: |
...
="com.google.android.gms.version" android:value="@integer/google_play_services_version" /> |
| Info |
|---|
The setting of the permission through the user is not mandatory, but highly recommended. If the permission If the permission is not set, only the Android ID is used. The last one item above is for the registration of google-play-services, which is precondition for retrieving Google Advertising ID. Two aspects are crucial: There is a bug in the Android version 2.2, which only occurs in connection with certain providers, where for all affected devices the same Android ID will be delivered. For the study, this would mean that the user identification would become much more difficult. |
Timeout
With this value, a timeout (in seconds) for each HTTP request can be configured within the library.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
SpringMobile spring = new ("app","TestApp",getApplicationContext());
spring.setTimeout(30); // in seconds
|
Advise for Implementation when using Android 3.0 and higher Versions
| Note |
|---|
Note: |
ProGuard
Therefore it is necessary to add the following lines into the ProGuard configuration file:
-keep class de.spring.** { *; }
-keep class de.spring.** { *; }
-keep class org.apache.** { *; }
If you want to suppress the warnings regarding library-program-class-dependencies , please add to the configuration file
-dontwarn android.webkit.WebView
-dontwarn android.webkit.WebViewClient
Implementation Blackberry
The following example shows the basic installation for the Blackberry platform. When generating the class SpringMobile a site identifier (<site>) has to be indicated, which is shipped together with this documentation and the libraries.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/**
* Importing SpringMobile
*/
import de.spring.mobile.SpringMobile;
/**
* Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and
* application name
*/
SpringMobile spring = new SpringMobile("<site>", "myApplication1");
/**
* Sending the start of the application to the measurement system
*/
Hashtable target = new Hashtable();
target.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_STARTED);
try {
// ...
spring.commit(target);
} catch (ParamNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* Sending the action spring.BACKGROUND
*/
Hashtable target = new Hashtable();
target.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUND);
try {
spring.commit(target);
} catch (ParamNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
 |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/**
* Alternative method
* Sending the action spring.BACKGROUND with own
* connection parameters
*/
Hashtable target = new Hashtable();
target.put(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUND);
Hashtable bbprops = new Hashtable();
bbprops.put("deviceside", "true");
try {
spring.commit(bbprops,target);
} catch (ParamNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
Example: Implementation of an app page request via the action variable (ac)
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/**
* example AC
*/
Hashtable target = new Hashtable();
target.put("ac", "Mainpage");
try {
// ...
spring.commit(target);
} catch (ParamNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
| Info |
|---|
Although the library provides the possiblity of using connection parameters, it is highly recommended to use "spring.commit(Hashtable target)". While using connection parameters that are not supported a respective exception is thrown. |
Implementation Windows Phone
The following example shows the basic installation for the Windows Phone 7 platform. When generating the class SpringMobile a site identifier (<site>) has to be indicated, which is shipped together with this documentation and the libraries.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/*
* Importing SpringMobile
*/
using spring_mobile_wp7;
/*
* Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and
* application name
*/
SpringMobile spring = new SpringMobile("<site>", "myApplication1");
/*
* Sending the start of the application to the measurement system
*/
Dictionary<String, String> target = new Dictionary<string, string>();
target.Add(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_STARTED);
spring.commit(target);
...
/*
* Sending the action spring.BACKGROUND
*/
Dictionary<String, String> target = new Dictionary<string, string>();
target.Add(SpringMobile.VAR_ACTION, SpringMobile.APP_BACKGROUND);
spring.commit(target);
|
Example: Implementation of an app page request via the action variable (ac)
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
/*
* Example AC
*/
using spring_mobile_wp7;
/*
* Generating SpringMobile entity with site id and application name
*/
SpringMobile spring = new SpringMobile("<site>", "myApplication1");
/*
* Sending AC to the measurement system
*/
Dictionary<String, String> target = new Dictionary<string, string>();
target.Add("ac", "Mainpage");
spring.commit(target);
...
/*
|
| Info | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
For the measurement we need the device ID. Please set the right for reading the device ID into a config file (WMAppManifest.xml).
|
Implementation Titanium (not supported at the moment)
| Include Page | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|